



Conductor marking lights are sometimes used (in conjunction with overhead wire markers) to make overhead power lines more visible. Because power lines are often suspended between widely-spaced masts, they present a particularly grave hazard to low flying aircraft.
Conductor marking lights are sometimes used (in conjunction with overhead wire markers) to make overhead power lines more visible. Because power lines are often suspended between widely-spaced masts, they present a particularly grave hazard to low flying aircraft. A simple and cost-effective solution to this problem is installing marking lights directly on the wires, but there are significant technical difficulties to low-cost power extraction from a distribution system which carries high voltages and wide-range AC current.
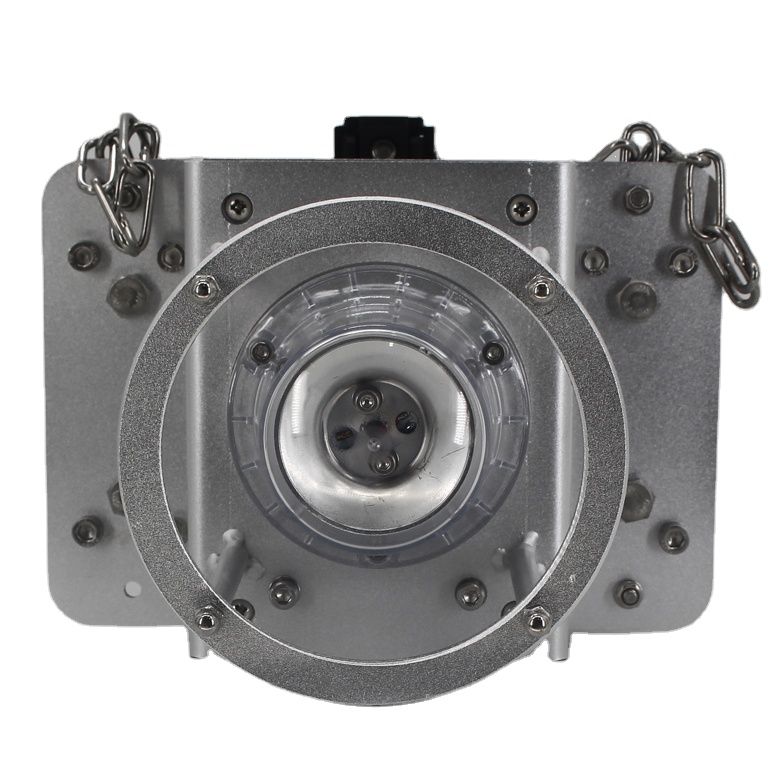
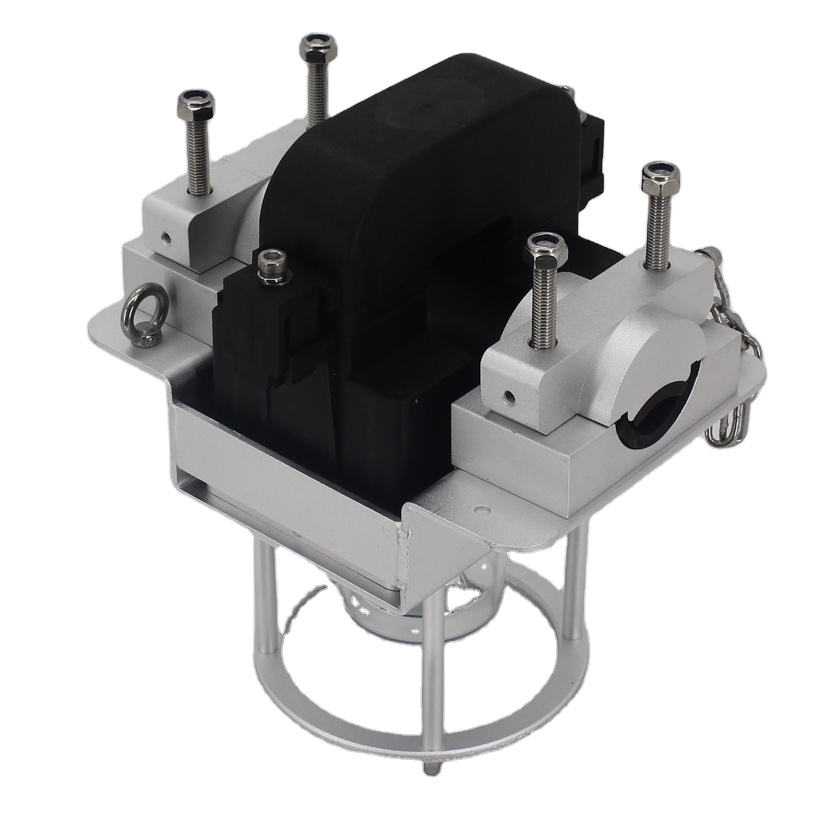
CK-11 Aviation Conduct Marking Light
1. Features and Parameters
1.1 Product Feature
l The product adopts LED light source, uses wire to induce power supply, and the interconnection is long.
l The product is light in weight, compact in design, and easy to install.
l Main purpose and scope of application: This product is mainly used as a warning on AC high voltage lines below 500KV.
l The light intensity, light color, and light emitting angle conform to the ICAO aviation obstruction light standard.

1.2 Technical Parameter
| Items Name | Parameter |
LED Source | LED |
Emitting Color | Red |
Horizontal beam angle | 360° |
Vertical beam angle | 10° |
Light Intensity | 15A<Conductor Current<50A,>10cd Conductor Current>50A, >32cd |
Adapt to wire voltage | AC 1-500KV |
Adapt to wire current | 15A-2000A |
LifeSpan | >100,000 hours |
Suitable high-voltage Conductor Diameter | 15-40mm |
Operating temperature | -40℃-+65℃ |
Relative humidity | 0%~95% |
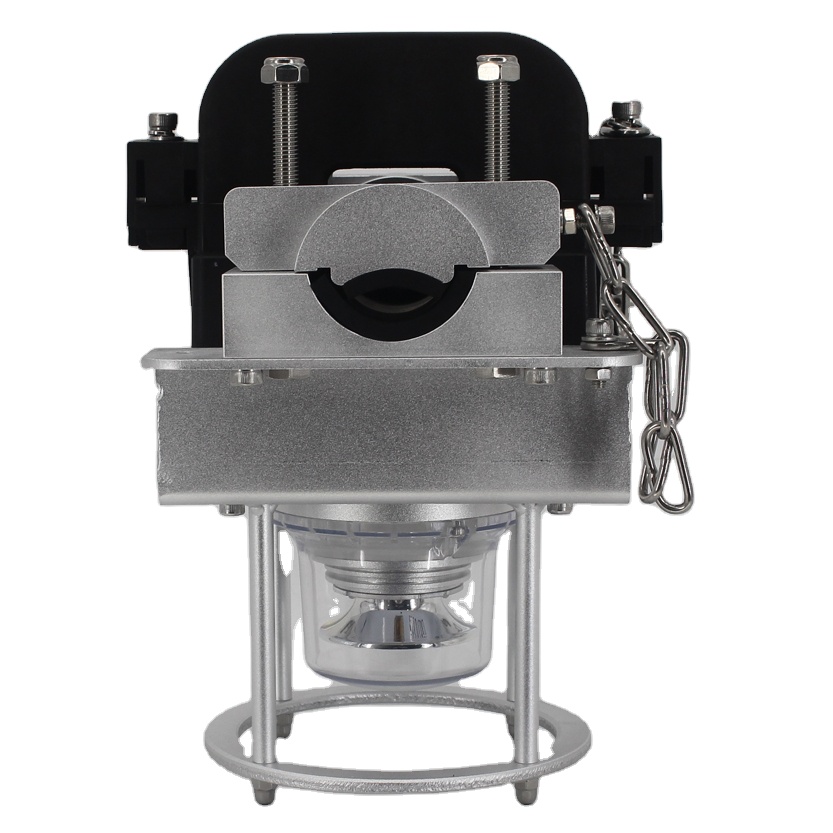

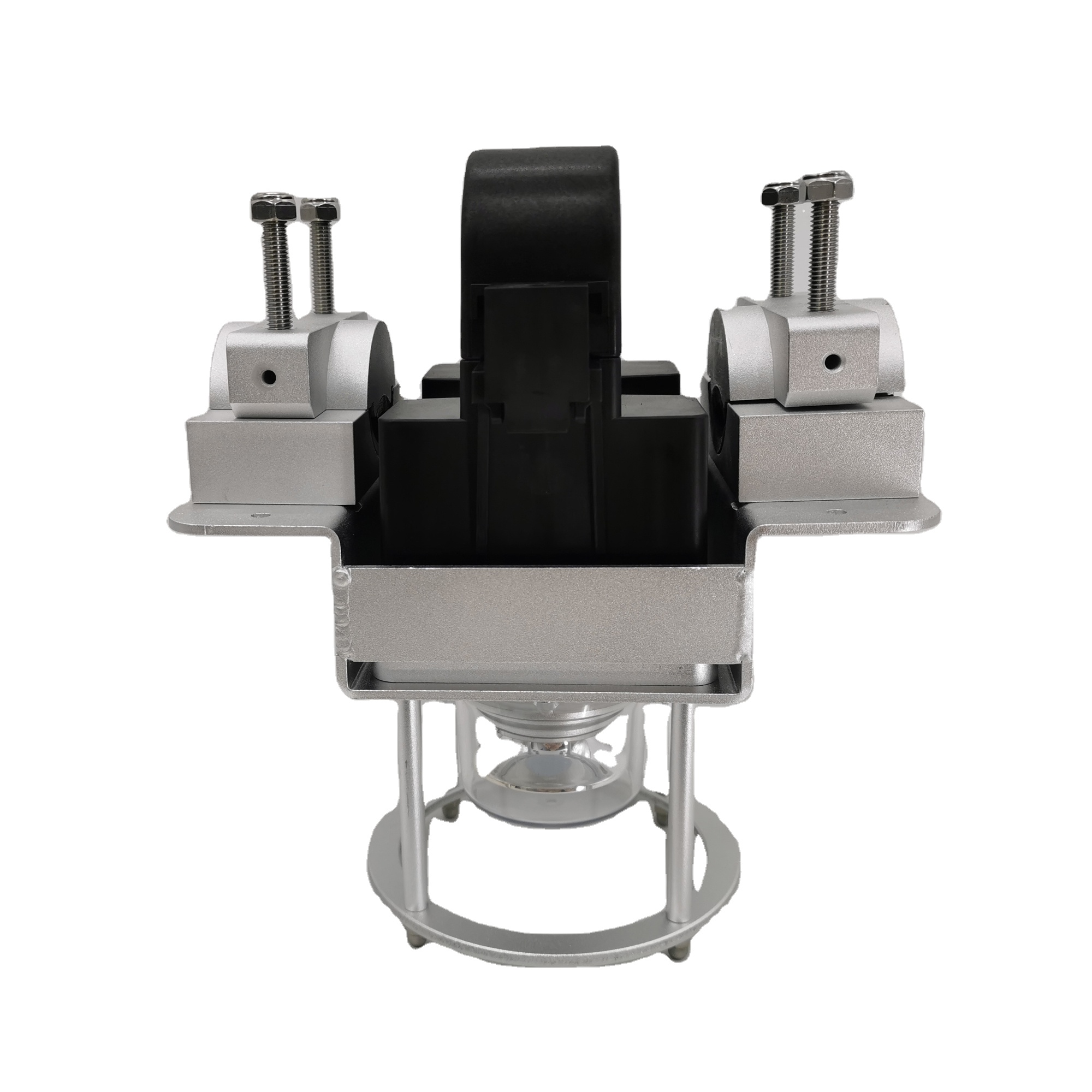
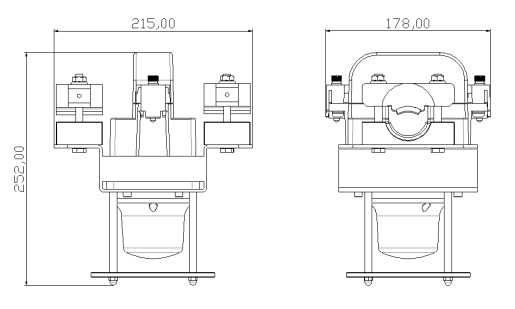
Overall Size and Gross weight:
L215mm*W178mm*H252mm,Gross Weight:4.1 KG
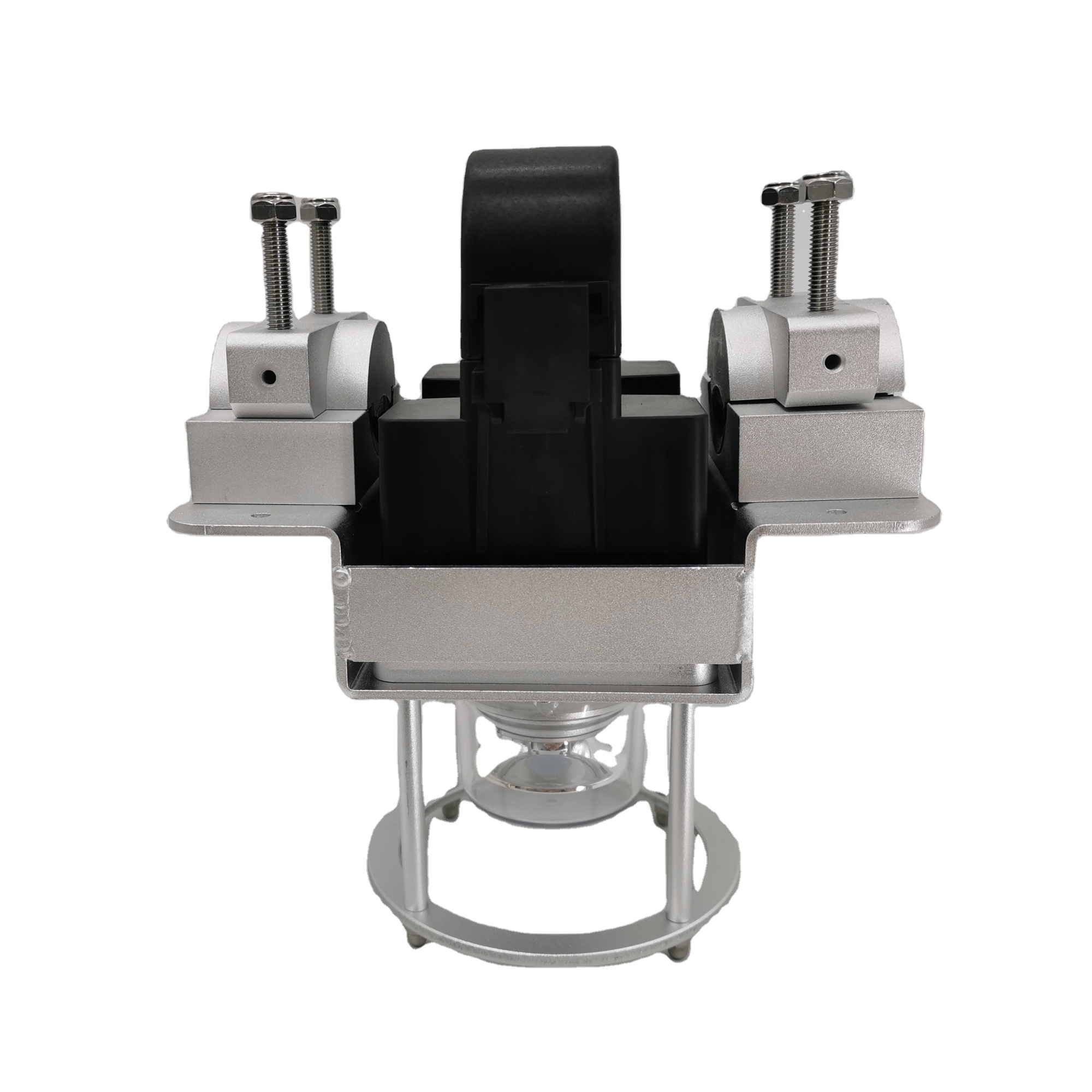
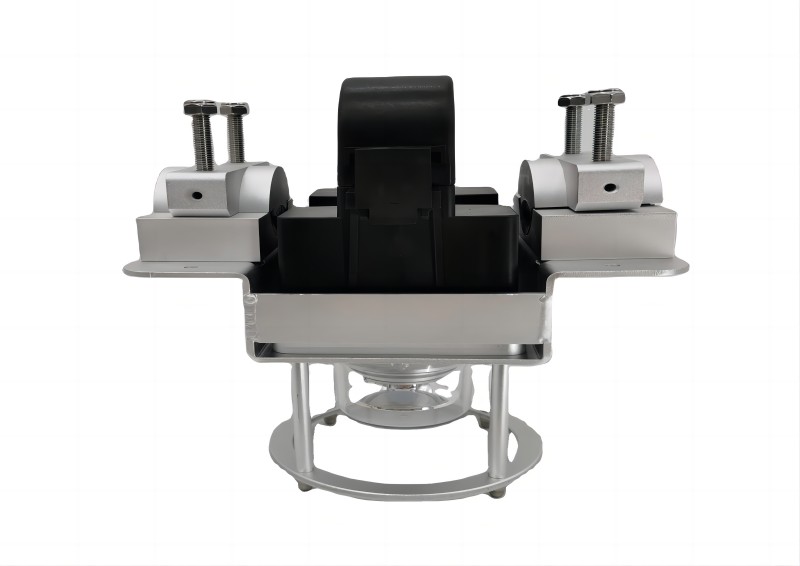
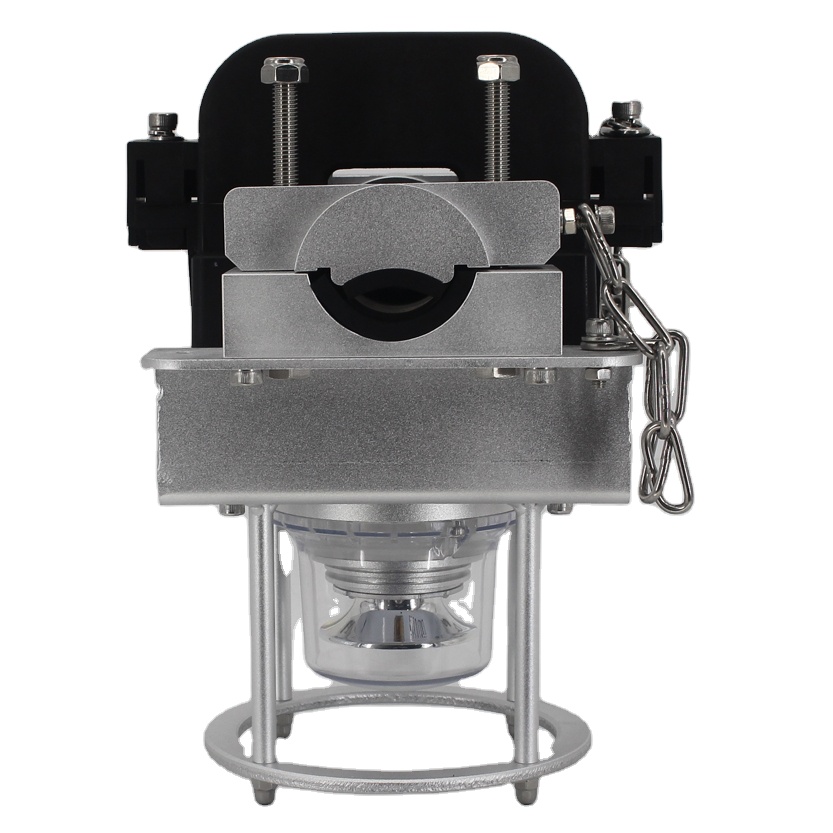
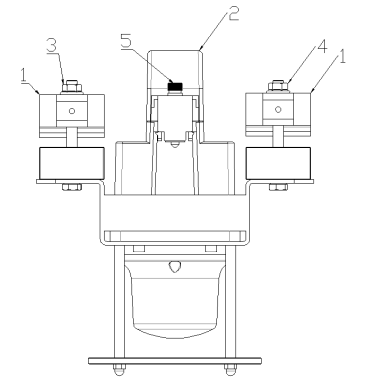
When the high-voltage line is out of power, separate the fastening parts 1, 2, and 3 of the product from the assembly of the product.
Bring the product close to the high-voltage line, and make the high-voltage line pass through the product's trunking.
Put the accessory 2 of the product into the main body of the product. The accessory should be fully assembled in place, and the screw 5 should be tightened.
Put the accessory 1 of the product into the original assembly position, and tighten the nuts 3 and 4. The product is fastened to the high-voltage line.
lNon-professionals are prohibited from working with electricity.
lThis product will heat up when it is working, which is normal.
lThis product is a sealed structure. Non-professional maintenance personnel should not disassemble or assemble it privately, so as not to affect its performance.
lWhen the product is working, it is strictly forbidden to open any part of the lamp body to prevent danger.
This lamp is a maintenance-free product. In the daily inspection process, if structural parts are found to be invalid or other abnormal phenomena, please replace them in time.
Remarks:Example of a magnetically-powered beacon based on a Rogowski coil (similar to a current transformer). This solution is usually intended for medium and high voltage lines up to 440 kV, but inductive coupling devices are able to work on any AC at 50 Hz or 60 Hz, from 15 up to 2000 Amps.
The ideal warning light must be able to power itself while clamped to a single wire of the line. Lights may be powered either from the electric field surrounding the energized wire, or the magnetic field produced by current through the wire. The first approach takes advantage of the high electric potential gradient between conductors, but a strong enough capacitive coupling is requested to allow capacitive extraction of the power required from the warning light. This means that long conductors must be suspended parallel to the line using glass/ceramic isolators: in fact several meters of suspended conductor are generally required, total length being inversely proportional to the line voltage. The second approach is based on Faraday's law of induction involving magnetic flux flowing through a circuit which powers the warning light.